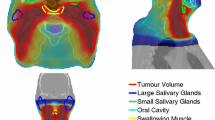
Abstract
Some row-action algorithms which exploit special objective function and constraints structure have proven advantageous for solving huge and sparse feasibility or optimization problems. Recently developed block-iterative versions of such special-purpose methods enable parallel computation when the underlying problem is appropriately decomposed. This opens the door for parallel computation in image reconstruction problems of computerized tomography and in the inverse problem of radiation therapy treatment planning, all in their fully discretized modelling approach. Since there is more than one way of deriving block-iterative versions of any row-action method, the choice has to be made with reference to the underlying real-world problem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Aharoni, A. Berman and Y. Censor, “An interior points algorithm for the convex feasibility problem,”Advances in Applied Mathematics 4 (1983) 479–489.
S. Agmon, “The relaxation method for linear inequalities,”Canadian Journal of Mathematics 6 (1954) 382–392.
M.D. Altschuler, Y. Censor, P.P.B. Eggermont, G.T. Herman, Y.H. Kuo, R.M. Lewitt, M. McKay, H.K. Tuy, J.K. Udupa and M.M. Yau, “Demonstration of a software package for the reconstruction of the dynamically changing structure of the human heart from cone beam X-ray projections,”Journal of Medical Systems 4 (1980) 289–304.
A. Auslender,Optimisation: Methods Numeriques (Masson, Paris, 1976).
L.M. Bregman, “The relaxation method of finding the common point of convex sets and its application to the solution of problems in convex programming,”USSR Computational Mathematics and Mathematical Physics 7 (1967) 200–217.
Y. Censor, “Row-action methods for huge and sparse systems and their applications,”SIAM Review 23 (1981) 444–466.
Y. Censor, “Finite series-expansion reconstruction methods,”Proceedings of the IEEE 71 (1983) 409–419.
Y. Censor, “An automatic relaxation method for solving interval linear inequalities,”Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 105 (1985) 19–25.
Y. Censor and A. Lent, “An iterative row-action method for interval convex programming,”Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications 34 (1981) 321–353.
Y. Censor and A. Lent, “Cyclic subgradient projections,”Mathematical Programming 24 (1982) 233–235.
Y. Censor and T. Elfving, “New methods for linear inequalities,”Linear Algebra and Its Applications 42 (1982) 199–211.
Y. Censor, P.P.B. Eggermont and D. Gordon, “Strong underrelaxation in Kaczmarz's method for inconsistent systems,”Numerische Mathematik 41 (1983) 83–92.
Y. Censor and G.T. Herman, “On some optimization techniques in image reconstruction from projections,”Applied Numerical Mathematics 3 (1987) 365–391.
Y. Censor, W. D. Powlis and M.D. Altschuler, “On the fully discretized model for the inverse problem of radiation therapy treatment planning,” in: K.R. Foster, ed.,Proceedings of the Thirteenth Annual Northeast Bioengineering Conference, Vol. 1 (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc., New York, 1987) pp. 211–214.
Y. Censor and A. Lent, “Optimization of ‘logx’ entropy over linear equality constrains,”SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization 25 (1987) 921–933.
Y. Censor, M.D. Altschuler and W.D. Powlis, “A computational solution of the inverse problem in radiation therapy treatment planning,”Applied Mathematics and Computation 25 (1988) 57–87.
Y. Censor and J. Segman, “On block-iterative entropy maximization,”Journal of Information and Optimization Sciences 8 (1987) 275–291.
Y. Censor, A.R. DePierro and A.N. Iusem, “On maximization of entropies and a generalization of Bregman's method for convex programming,” Technical Report MIPG 113, September 1986.
Y. Censor, M.D. Altschuler and W.D. Powlis, “On the use of Cimmino's simultaneous projections methods for computing a solution of the inverse problem in radiation therapy treatment planning,”Inverse Problems (1988), in print.
Y. Censor, A.R. DePierro, T. Elfving, G.T. Herman and A.N. Iusem, “On iterative methods for linearly constrained entropy maximization,” in: A. Wakulicz, ed.,Numerical Analysis and Mathematical Modelling, Banach Center Publications, Vol. XXIV, Stefan Banach International Mathematical Center, Warsaw, 1988, in print.
G. Cimmino, “Calcolo Approssimato per le Soluzioni dei Sistemi di Equazioni Lineari,”La Ricerca Scientifica, Roma XVI, Ser. II, Anno IX, Vol. 1, pp. 326–333, 1938.
J.N. Darroch and D. Ratcliff, “Generalized iterative scaling for log-linear models,”The Annals of Mathematical Statistics 43 (1972) 1470–1480.
A.R. De Pierro and A.N. Iusem, “A simultaneous projection method for linear inequalities,”Linear Algebra and Its Applications 64 (1985) 243–253.
P.P.B. Eggermont, G.T. Herman and A. Lent, “Iterative algorithms for large partitioned linear systems, with applications to image reconstruction,”Linear Algebra and Its applications 40 (1981) 37–67.
T. Elfving, “Block-iterative methods for consistent and inconsistent linear equations,”Numerische Mathematik 35 (1980) 1–12.
I.I. Eremin, “On some iterative methods in convex programming,”Ekonomika i Matematichesky Methody 2 (1966) 870–886 (In Russian).
I.I. Eremin, “Fejer mappings and convex programming,”Siberian Mathematical Journal 10 (1969) 762–772.
A. George, G.W. Stewart and R. Voigt (Editors), “Special Volume of Linear Algebra and Its Applications on Parallel Computing,”Linear Algebra and Its Applications, Vol. 77, May 1986.
P. Gilbert, “Iterative methods for the three-dimensional reconstruction of an object from projections,”Journal of Theoretical Biology 36 (1972) 105–117.
R. Gordon, R. Bender and G.T. Herman, “Algebraic reconstruction techniques (ART) for three-dimensional electron microscopy and X-ray photography,”Journal of Theoretical Biology 29 (1970) 471–481.
R. Gordon and G.T. Herman, “Three-dimensional reconstruction from projections: A review of algorithms,”International Review of Cytology 38 (1974) 111–151.
L.G. Gubin, B.T. Polyak and E.V. Raik, “The method of projections for finding the common point of convex sets,”USSR Computational Mathematics and Mathematical Physics 7 (1967) 1–24.
G.T. Herman, “A relaxation method for reconstructing objects from noisy X-rays,”Mathematical Programming 8 (1975) 1–19.
G.T. Herman,Image Reconstruction from Projections: The Fundamentals of Computerized Tomography (Academic Press, New York, 1980).
G.T. Herman and A. Lent, “Iterative reconstruction algorithms,”Computers in Biology and Medicine 6 (1976) 273–294.
G.T. Herman, A. Lent and P.H. Lutz, “Iterative relaxation methods for image reconstruction,”Communications of the ACM 21 (1978) 152–158.
G.T. Herman and A. Lent, “A family of iterative quadratic optimization algorithms for pairs of inequalities with application in diagnostic radiology,”Mathematical Programming Study 9 (1978) 15–29.
G.T. Herman, H. Levkowitz, H.K. Tuy and S. McCormick, “Multilevel image reconstruction,” in: A. Rosenfeld, ed.,Multiresolution Image Processing and Analysis (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, Tokyo, 1984) pp. 121–135.
G.T. Herman and H. Levkowitz, “Initial performance of block-iterative reconstruction algorithms,” in M.A. Viergever and A. Todd-Porkopek, eds.,Mathematics and Computer Science of Medical Imaging (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, Tokyo, 1987) pp. 305–318.
C. Hildreth, “A quadratic programming procedure,”Naval Research Logistics Quarterly 4 (1957) 79–85. Erratum,Ibid, p. 361.
E.B. Hinkle, J.L.C. Sanz, A.K. Jain and D. Petkovic, “P 3 E: New Life for projection-based image processing,”Jorunal of Parallel and Distributed Computing 4 (1987) 45–78.
A.N. Iusem and A.R. De Pierro, “Convergence results for an accelerated nonlinear Cimmino algorithm,”Numerische Mathematik 49 (1986) 367–378.
A.N. Iusem and A.R. De Pierro, “A simultaneous iterative method for computing projections on polyhedra,”SIAM Journal of Control and Optimization 25 (1987) 231–243.
L.H. Jamieson and S.L. Tanimoto, “Special issue on parallel image processing and pattern recognition: Guest editors' introduction,”Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 4 (1987) 1–6.
S. Kaczmarz, “Angenäherte Auflösung von Systemen Linearer Gleichungen,”Bull. Acad. Polon. Sci. Lett. A. 35 (1937) 355–357.
A.V. Lakshminarayanan and A. Lent, “Methods of least squares and SIRT in reconstruction,”Journal of Theoretical Biology 76 (1979) 267–295.
A. Lent, “A convergent algorithm for maximum entropy image restoration with a medical X-ray application,” in: R. Shaw, ed.,Image Analysis and Evaluation (Society of Photographic Scientists and Engineers, SPSE, Washington, DC, 1977), pp. 249–257.
A. Lent, Private discussions, July 1987.
A. Lent and Y. Censor, “Extensions of Hildreth's row-action method for quadratic programming,”SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization 18 (1980) 444–454.
R.M. Lewitt, “Reconstruction algorithms: Transform methods,”Proceedings of the IEEE 71 (1983) 390–408.
F.A. Lootsma and K.M. Ragsdell, “State-of-the-art in parallel nonlinear optimization,”Parallel Computing, 6 (1988) 133–155.
J.M. Martinez and R.J.B. De Sampaio, “Parallel and sequential Kaczmarz methods for solving underdetermined nonlinear equations,”Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics 15 (1986) 311–321.
S.F. McCormick, “The method of Kaczmarz and row orthogonalization for solving linear equations and least squares problems in Hilbert space,”Indiana University Mathematics Journal 26 (1977) 1137–1150.
Y.I. Merzlyakov, “On a relaxation method of solving systems of linear inequalities,”USSR Computational Mathematics and Mathematical Physics 3 (1963) 504–510.
T.S. Motzkin and I.J. Schoenberg, “The relaxation method for linear inequalities,”Canadian Journal of Mathematics 6 (1954) 393–404.
F. Natterer,The Mathematics of Computerized Tomography (B.G. Teubner, Stuttgart, 1986).
L.A. Shepp and Y. Vardi, “Maximum likelihood reconstruction in positron emission tomography,”IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging MI-1 (1982) 113–122.
K. Tanabe, “Projection method for solving a singular system of linear equations and its applications,”Numerische Mathematik 17 (1971) 203–214.
P. Tseng and D.P. Bertsekas, “Relaxation methods for problems with strictly convex separable costs and linear constraints,”Mathematical Programming 38 (1987) 303–321.
Y. Vardi, L.A. Shepp and L. Kaufman, “A statistical model for positron emission tomography,”Journal of the American Statistical Association 80 (1985) 8–37.
S.A. Zenios, Private discussions, April 1987.
A.R. De Pierro and A.N. Iusem, “A relaxed version of Bregman's method for convex programming“,Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications 51 (1986) 421–440.
R. Aharoni and Y. Censor, “Block-iterative projection methods for parallel computation of solutions to convex feasibility problems”, Technical Report, June 1988.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was done with partial support of National Institutes of Health, Grant HL-28438 while the author was with the Medical Image Processing Group (MIPG) at the Department of Radiology, Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, USA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Censor, Y. Parallel application of block-iterative methods in medical imaging and radiation therapy. Mathematical Programming 42, 307–325 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01589408
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01589408