Summary.
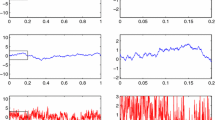
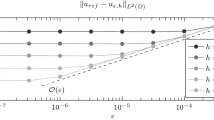
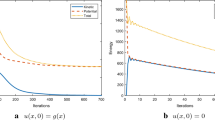
The reliability of frequently applied averaging techniques for a posteriori error control has recently been established for a series of finite element methods in the context of second-order partial differential equations. This paper establishes related reliable and efficient a posteriori error estimates for the energy-norm error of an obstacle problem on unstructured grids as a model example for variational inequalities. The surprising main result asserts that the distance of the piecewise constant discrete gradient to any continuous piecewise affine approximation is a reliable upper error bound up to known higher order terms, consistency terms, and a multiplicative constant.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainsworth, M., Oden, J.T.: A posteriori error estimation in finite element analysis. John Wiley & Sons, xx+240, 2000
Alberty, J.: Carsten Carstensen and Stefan A. Funken. Remarks around 50 lines of Matlab: short finite element implementation. Numer Algorithms 20(2–3), 117–137 (1999)
Babuška, I., Strouboulis, T.: The finite element method and its reliability. Oxford University Press, xii+802, 2001
Bartels, S., Carstensen, C.: Each averaging technique yields reliable a posteriori error control in FEM on unstructured grids. Part II: higher order FEM. Math. Comp. 71(239), 971–994 (2002)
Bartels, S.: Carsten Carstensen and Georg Dolzmann. Inhomogeneous Dirichlet conditions in a priori and a posteriori finite element error analysis. Numer. Math. (in press). Preprint available at http://www.numerik.uni-kiel.de/reports/2002/02-1.html
Blum, H., Suttmeier, F-T.: Weighted error estimates for finite element solutions of variational inequalities. Computing 65(2), 119–134 (2000)
Brenner, S.C., L. Ridgway Scott. The mathematical theory of finite element methods. Springer Verlag, New York, 15, xii+294, 1994
Carstensen, C.: Quasi interpolation and a posteriori error analysis in finite element method. M2AN Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 33(6), 1187–1202 (1999)
Carstensen, C.: All first-order averaging techniques for a posteriori finite element error control on unstructured grids are efficient and reliable. Math. Comp. 73(247), 1153–1165 (2004)
Carstensen, C., Alberty, J.: Averaging techniques for reliable a posteriori FE-error control in elastoplasticity with hardening. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 192(11–12), 1435–1450 (2003)
Carstensen, C., Bartels, S.: Each averaging technique yields reliable a posteriori error control in FEM on unstructured grids. I. Low order conforming, nonconforming and Mixed FEM. Math. Comp. 71(239), 945–969 (2002)
Carstensen, C., Funken, S.A.: Constants in Clement-interpolation error and residual based a posteriori estimates in finite element methods. East-West J. Numer. Math. 8(3), 153–175 (2000)
Carstensen, C., Funken, S.A.: Averaging technique for FE a posteriori error control in elasticity. Part I: conforming FEM. Comp. Meth. Appl. Engrg. 190, 2483–2498 (2001); II. λ-independend estimates. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 190(35–36), 4663–4675 (2001); III. Locking-free nonconforming FEM. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 191(8-10), 861–877 (2001)
Carstensen, C., Funken, S.A.: A posteriori error control in low-order finite element discretisations of incompressible stationary flow problems. Math. Comp. 70(236), 1353–1381 (2001)
Carstensen, C., Verfürth, R.: Edge residuals dominate a posteriori error estimates for low order finite element methods. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 36(5), 1571–1587 (1999)
Chen, Z., Nochetto, R.H.: Residual type a posteriori error estimates for elliptic obstacle problems. Numer. Math. 84(4), 527–548 (2000)
Ciarlet, P.G.: The finite element method for elliptic problems. North-Holland Publishing Co. Amsterdam, xix+530, 1978
Clément, P.: Approximation by finite element functions using local regularization. Rev. Française Automat. Informat. Recherche Opérationnelle Sér. Rouge Anal. Numér. 9(R-2), 77–84 (1975)
Elliott, C.M.: On the finite element approximation of an elliptic variational inequality arising from an implicit time discretization of the Stefan problem. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 1(1), 115–125 (1981)
Eriksson, K., Estep, D.J., Hansbo, P., Johnson, C.: Introduction to adaptive methods for differential equations. Acta Numerica, 1995, Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, 1995, pp. 105–158
Evans, L.C., Gariepy, R.F.: Measure theory and fine properties of functions. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, viii+268, 1992
Falk, R.S.: Error estimates for the approximation of a class of variational inequalities. Math. Comput. 28, 963–971 (1974)
Glowinski, R., Lions, J-L., Tremolieres, R.: Numerical analysis of variational inequalities. (Studies in Mathematics and its Applications) North-Holland Publishing Co. Amsterdam, 8, 1981
Kornhuber, R., Adaptive monotone multigrid methods for nonlinear variational problems. (Advances in Numerical Mathematics) B.G.Teubner, Stuttgart, 158, 1997
Li, R., Liu, W., Tang, T.: Moving Mesh Finite Element Approximations for Variational Inequality I: Static Obstacle Problems. Preprint 277 of Department of Mathematics, Hong Kong Baptist University, 2000
Natterer, F.: Optimale L2-Konvergenz finiter Elemente bei Variationsungleichungen. Bonner Math. Schr. 89, 1–12 (1976)
Nochetto, R.H., Wahlbin, L.B.: Positivity preserving finite element interpolation. Math. Comput. 71(240), 1405–1419 (2002)
Rodrigues, J.F.: Obstacle problems in mathematical physics. North Holland Publishing Co. Amsterdam, xvi+352, 1987
Veeser, A.: On a posteriori error estimation for constant obstacle problems. (Numerical methods for viscosity solutions and applications (Heraklion, 1999)), Ser. Adv. Math. Appl. Sci. World Sci. Publishing, 59, 221–234 (2001)
Veeser, A.: Efficient and reliable a posteriori error estimators for elliptic obstacle problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 39(1), 146–167 (2001)
Verfürth, R.: A review of a posteriori error estimation and adaptive mesh- refinement techniques. Wiley-Teubner, 1996
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Mathematics Subject Classification (2000): 35J20, 49J40, 65N30
Acknowledgement The first author (S.B.) thankfully acknowledges partial support by the German Research Foundation (DFG) within the Graduiertenkolleg ‘Effiziente Algorithmen und Mehrskalenmethoden’. The authors thank one anonymous referee for the suggestion of an projected SOR algorithm.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bartels, S., Carstensen, C. Averaging techniques yield reliable a posteriori finite element error control for obstacle problems. Numer. Math. 99, 225–249 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00211-004-0553-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00211-004-0553-6