Abstract
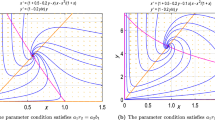
Global bifurcation analysis of a class of general predator–prey models with a strong Allee effect in prey population is given in details. We show the existence of a point-to-point heteroclinic orbit loop, consider the Hopf bifurcation, and prove the existence/uniqueness and the nonexistence of limit cycle for appropriate range of parameters. For a unique parameter value, a threshold curve separates the overexploitation and coexistence (successful invasion of predator) regions of initial conditions. Our rigorous results justify some recent ecological observations, and practical ecological examples are used to demonstrate our theoretical work.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguirre P, González-Olivares E, Sáez E (2009) Three limit cycles in a Leslie-Gower predator-prey model with additive Allee effect. SIAM J Appl Math 69(5): 1244–1262
Albrecht F, Gatzke H, Wax N (1973) Stable limit cycles in prey-predator populations. Science 181: 1074–1075
Albrecht F, Gatzke H, Haddad A, Wax N (1974) The dynamics of two interacting populations. J Math Anal Appl 46: 658–670
Allee WC (1931) Animal aggregations: a study in general sociology. University of Chicago Press
Alexander JC, Yorke JA (1978) Global bifurcations of periodic orbits. Am J Math 100: 263–292
Arditi R, Ginzburg LR (1989) Coupling in predator-prey dynamics: ratio-dependence. J Theor Biol 139: 311–326
Bazykin AD (1998) Nonlinear dynamics of interacting populations. World Scientific Series on nonlinear science. Series A: monographs and treatises, 11. World Scientific Publishing Co., Inc., River Edge
Berec L, Angulo E, Courchamp F (2007) Multiple Allee effects and population management. Trends Ecol Evol 22: 185–191
Boukal SD, Berec L (2002) Single-species models of the Allee effect: extinction boundaries, sex ratios and mate encounters. J Theor Biol 218: 375–394
Boukal SD, Sabelis WM, Berec L (2007) How predator functional responses and Allee effects in prey affect the paradox of enrichment and population collapses. Theor Popul Biol 72: 136–147
Burgman MA, Ferson S, Akcakaya HR (1993) Risk assessment in conservation biology. Chapman and Hall, London
Cheng KS (1981) Uniqueness of a limit cycle for a predator-prey system. SIAM J Math Anal 12: 541–548
Chow SN, Mallet-Paret J (1978) The Fuller index and global Hopf bifurcation. J Differ Equ 29: 66–85
Conway ED, Smoller JA (1986) Global analysis of a system of predator-prey equations. SIAM J Appl Math 46: 630–642
Courchamp F, Clutton-Brock T, Grenfell B (1999) Inverse density dependence and the Allee effect. Trends Ecol Evol 14: 405–410
Courchamp F, Berec L, Gascoigne J (2008) Allee effects in ecology and conservation. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Dennis B (1989) Allee effect: population growth, critical density, and chance of extinction. Nat Resour Model 3: 481–538
Dhooge A, Govaerts W, Kuznetsov YA (2003) MATCONT: a MATLAB package for numerical bifurcation analysis of ODEs. ACM Trans Math Softw 29: 141–164
Edelstein KL (1998) Mathematical models in biology. Random House, New York
Gascoigne JC, Lipcius RN (2004) Allee effects driven by predation. J Appl Ecol 41: 801–810
González-Olivares E, González-Yaez B, Sáez E, Szántó I (2006) On the number of limit cycles in a predator prey model with non-monotonic functional response. Discrete Contin Dyn Syst B 6(3): 525–534
Gruntfest Y, Arditi R, Dombrovsky Y (1997) A fragmented population in a varying environment. J Theor Biol 185: 539–547
Hassard BD, Kazarinoff ND, Wan Y (1981) Theory and applications of Hopf bifurcation. London Math Soc Lecture Note Ser, vol 41. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Hilker FM, Langlais M, Malchow H (2009) The Allee effect and infectious diseases: extinction, multistability, and the (dis-)appearance of oscillations. Am Nat 173: 72–88
Holling CS (1959) The components of predation as revealed by a study of small mammal predation of the European Pine Sawfly. Can Entomol 91: 293–320
Hsu SB (1978) On global stability of a predator-prey system. Math Biosci 39: 1–10
Hsu SB (2006) Ordinary differential equations with applications. Series on Applied Mathematics, vol 16. World Scientific Publishing Co., Hackensack
Hsu SB, Shi J (2009) Relaxation oscillator profile of limit cycle in predator-prey system. Discrete Contin Dyn Syst B 11(4): 893–911
Hsu SB, Hwang TW, Kuang Y (2001) Global analysis of the Michaelis-Menten-type ratio-dependent predator-prey system. J Math Biol 42: 489–506
Ivlev VS (1955) Experimental ecology of the feeding of fishes. Yale University Press
Jacobs J (1984) Cooperation, optimal density and low density thresholds: yet another modification of the logistic model. Oecologia 64: 389–395
Jiang J, Shi J (2009) Bistability dynamics in some structured ecological models. In: Spatial ecology. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Kazarinov N, van den Driessche P (1978) A model predator-prey systems with functional response. Math Biosci 39: 125–134
Kuang Y, Beretta E (1998) Global qualitative analysis of a ratio-dependent predator-prey system. J Math Biol 36: 389–406
Kuang Y, Freedman HI (1988) Uniqueness of limit cycles in Gause-type models of predator-prey systems. Math Biosci 88: 67–84
Kuznetsov YA (2004) Elements of applied bifurcation theory. Appl Math Sci, vol 112. Springer-Verlag, New York
Lande R (1987) Extinction thresholds in demographic models of territorial populations. Am Nat 130: 624–635
Lewis MA, Kareiva P (1993) Allee dynamics and the spread of invading organisms. Theor Popul Biol 43: 141–158
Lotka AJ (1925) Elements of physical biology. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore
Malchow H, Petrovskii SV, Venturino E (2008) Spatiotemporal patterns in ecology and epidemiology. Theory, models, and simulation. Chapman & Hall/CRC Mathematical and Computational Biology Series. Chapman & Hall, Boca Raton
May RM (1972) Limit cycles in predator-prey communities. Science 177: 900–902
Morozov A, Petrovskii S, Li B-L (2004) Bifurcations and chaos in a predator-prey system with the Allee effect. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 271: 1407–1414
Morozov A, Petrovskii S, Li B-L (2006) Spatiotemporal complexity of patchy invasion in a predator-prey system with the Allee effect. J Theor Biol 238(1): 18–35
Owen MR, Lewis MA (2001) How predation can slow, stop or reverse a prey invasion. Bull Math Biol 63: 655–684
Petrovskii SV, Morozov A, Venturino E (2002) Allee effect makes possible patchy invasion in a predator-prey system. Ecol Lett 5: 345–352
Petrovskii S, Morozov A, Li B-L (2005) Regimes of biological invasion in a predator-prey system with the Allee effect. Bull Math Biol 67(3): 637–661
Polking JA, Arnold D (2003) Ordinary differential equations using MATLAB, 3rd edn. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Rosenzweig ML (1969) Why the prey curve has a hump? Am Nat 103: 81–87
Rosenzweig LM (1971) Paradox of enrichment: destabilization of exploitation ecosystems in ecological time. Science 171(3969): 385–387
Rosenzweig ML, MacArthur R (1963) Graphical representation and stability conditions of predator-prey interactions. Am Nat 97: 209–223
Ruan S, Xiao D (2000) Global analysis in a predator-prey system with nonmonotonic functional response. SIAM J Appl Math 61: 1445–1472
Shi J, Shivaji R (2006) Persistence in reaction diffusion models with weak Allee effect. J Math Biol 52: 807–829
Stephens PA, Sutherland WJ (1999) Consequences of the Allee effect for behaviour, ecology and conservation. Trends Ecol Evol 14: 401–405
Stephens PA, Sutherland WJ, Freckleton RP (1999) What is the Allee effect? Oikos 87: 185–190
Takeuchi Y (1996) Global dynamical properties of Lotka-Volterra systems. World Scientific, Singapore
Thieme HR, Dhirasakdanon T, Han Z, Trevino R (2009) Species decline and extinction: synergy of infectious disease and Allee effect? J Biol Dyn 3: 305–323
Turchin P (2003) Complex population dynamics: a theoretical/empirical synthesis. Princeton University Press
van Voorn GAK, Hemerik L, Boer MP, Kooi BW (2007) Heteroclinic orbits indicate overexploitation in predator prey systems with a strong Allee effect. Math Biosci 209: 451–469
Volterra V (1926) Fluctuations in the abundance of species, considered mathmatically. Nature 118: 558
Wang ME, Kot M (2001) Speeds of invasion in a model with strong or weak Allee effects. Math Biosci 171: 83–97
Wiggins S (1990) Introduction to applied nonlinear dynamical systems and chaos. Texts Appl Math, vol 2. Springer, New York
Wilson EO, Bossert WH (1971) A primer of population biology. Sinauer Assoxiates, Sunderland
Wu J (1998) Symmetric functional-differential equations and neural networks with memory. Trans Am Math Soc 350: 4799–4838
Xiao D, Ruan S (2001) Global dynamics of a ratio-dependent predator-prey system. J Math Biol 43: 268–290
Xiao D, Zhang Z (2003) On the uniqueness and nonexistence of limit cycles for predator-prey system. Nonlinearity 16: 1–17
Xiao D, Zhang Z (2008) On the existence and uniqueness of limit cycles for generalized Liénard systems. J Math Anal Appl 343: 299–309
Zeng X, Zhang Z, Gao S (1994) On the uniqueness of the limit cycle of the generalized Liénard equation. Bull Lond Math Soc 26: 213–247
Zhang ZF (1986) Proof of the uniqueness theorem of limit cycles of generalized Liénard equations. Appl Anal 23(1–2): 63–76
Zhou SR, Liu YF, Wang G (2005) The stability of predator-prey systems subject to the Allee effects. Theor Popul Biol 67(1): 23–31
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No 10771045, 10671049) and Program of Excellent Team in HIT, National Science Foundation of US, and Longjiang professorship of Department of Education of Heilongjiang Province.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Shi, J. & Wei, J. Predator–prey system with strong Allee effect in prey. J. Math. Biol. 62, 291–331 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-010-0332-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-010-0332-1