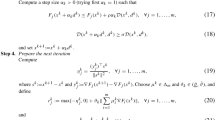Abstract
This article presents a branch-reduction-bound algorithm for globally solving the generalized geometric programming problem. To solve the problem, an equivalent monotonic optimization problem whose objective function is just a simple univariate is proposed by exploiting the particularity of this problem. In contrast to usual branch-and-bound methods, in the algorithm the upper bound of the subproblem in each node is calculated easily by arithmetic expressions. Also, a reduction operation is introduced to reduce the growth of the branching tree during the algorithm search. The proposed algorithm is proven to be convergent and guarantees to find an approximative solution that is close to the actual optimal solution. Finally, numerical examples are given to illustrate the feasibility and efficiency of the present algorithm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hansen P., Jaumard B.: Reduction of indefinite quadratic programs to bilinear programs. J. Global Optim. 2(1), 41–60 (1992)
Beightler C.S., Phillips D.T.: Applied Geometric Programming. Wiley, New York, NY (1976)
Avriel M., Williams A.C.: An extension of geometric programming with applications in engineering optimization. J. Eng. Math. 5(3), 187–199 (1971)
Jefferson T.R., Scott C.H.: Generalized geometric programming applied to problems of optimal control: I.theory. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 26, 117–129 (1978)
Nand K.J.: Geometric programming based robot control design. Comput. Ind. Eng. 29(1–4), 631–635 (1995)
Das K., Roy T.K., Maiti M.: Multi-item inventory model with under imprecise objective and restrictions: a geometric programming approach. Prod. Plan. Control 11(8), 781–788 (2000)
Jae Chul C., Bricker Dennis L.: Effectiveness of a geometric programming algorithm for optimization of machining economics models. Comput. Oper. Res. 23(10), 957–961 (1996)
EI Barmi H., Dykstra R.L.: Restricted multinomial maximum likelihood estimation based upon Fenchel duality. Stat. Probab. Lett. 21, 121–130 (1994)
Bricker, D.L., Kortanek, K.O., Xu, L.: Maximum linklihood estimates with order restrictions on probabilities and odds ratios: a geometric programming approach. Applied Mathematical and Computational Sciences, University of IA, Iowa City, IA (1995)
Jagannathan R.: A stochastic geometric programming problem with multiplicative recourse. Oper. Res. Lett. 9, 99–104 (1990)
Maranas C.D., Floudas C.A.: Global optimization in generalized geometric programming. Comput. Chem. Eng. 21(4), 351–369 (1997)
Rijckaert M.J., Matens X.M.: Analysis and optimization of the Williams-Otto process by geometric programming. AICHE J. 20(4), 742–750 (1974)
Ecker J.G.: Geometric programming: methods, computations and applications. SIAM Rev. 22(3), 338–362 (1980)
Kortanek K.O., Xiaojie X., Yinyu Y.: An infeasible interior-point algorithm for solving primal and dual geometric programs. Math. Program. 76, 155–181 (1996)
Passy U.: Generalized weighted mean programming. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 20, 763–778 (1971)
Passy U., Wilde D.J.: Generalized polynomial optimization. J. Appl. Math. 15(5), 1344–1356 (1967)
Wang Y., Zhang K., Gao Y.: Global optimization of generalized geometric programming. Appl. Math. Comput. 48, 1505–1516 (2004)
Qu S., Zhang K., Wang F.: A global optimization using linear relaxation for generalized geometric programming. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 190, 345–356 (2008)
Shen P., Zhang K.: Global optimization of signomial geometric programming using linear relaxation. Appl. Math. Comput. 150, 99–114 (2004)
Qu S., Zhang K., Ji Y.: A new global optimization algorithm for signomial geometric programming via Lagrangian relaxation. Appl. Math. Comput. 182(2), 886–894 (2007)
Wang Y., Liang Z.: A deterministic global optimization algorithm for generalized geometric programming. Appl. Math. Comput. 168, 722–737 (2005)
Shen P., Jiao H.: A new rectangle branch-and-pruning approach for generalized geometric programming. Appl. Math. Comput. 183, 1027–1038 (2006)
Sherali H.D., Tuncbilek C.H.: A global optimization algorithm for polynomial programming problems using a formulation-linearzation technique. J. Glob. Optim. 2, 101–112 (1992)
Sherali H.D.: Global optimization of nonconvex polynomial programming problems having rational exponents. J. Glob. Optim. 12, 267–283 (1998)
Gounaris C.E., Floudas C.A.: Convexity of products of univariate functions and convexification transformations for geometric programming. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 138, 407–427 (2008)
Lu H.C., Floudas C.A.: Convex relaxation for solving posynomial programs. J. Glob. Optim. 46, 147–154 (2010)
Tsai J.F., Lin M.H.: An efficient global approach for posynomial geometric programming problems. INFORMS J. Comput. 23(3), 483–492 (2011)
Wang Y., Li T., Liang Z.: A general algorithm for solving generalized geometric programming with nonpositive degree of difficulty. Comput. Optim. Appl. 44, 139–158 (2009)
Shen P., Ma Y., Chen Y.Y.: A robust algorithm for generalized geometric programming. J. Glob. Optim. 41, 593–612 (2008)
Tuy H.: Polynomial optimization: a robust approach. Pac. J. Optim. 1, 357–374 (2005)
Porn R., Bjork K.M., Westerlund T.: Global solution of optimization of problems with signomial parts. Discrete Optim. 5, 108–120 (2008)
Lundell A., Westerlund T.: Convex underestimation strategies for signomial functions. Optim. Methods Softw. 24, 505–522 (2009)
Lundell A., Westerlund J., Westerlund T.: Some transformation techniques with applications in global optimization. J. Glob. Optim. 43, 391–405 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Research supported by NSFC (11171094; 11171368) and Innovation Scientists and Technicians Troop Construction Projects of Henan Province (114200510011).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, P., Li, X. Branch-reduction-bound algorithm for generalized geometric programming. J Glob Optim 56, 1123–1142 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10898-012-9933-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10898-012-9933-0