Abstract
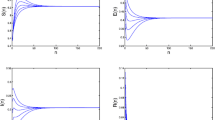
In this paper, an SEIRS epidemic model with a saturation incidence rate and a time delay describing a latent period is investigated. By analyzing the corresponding characteristic equations, the local stability of an endemic equilibrium and a disease-free equilibrium is established. When the basic reproduction number is greater than unity, by means of an iteration technique, sufficient conditions are obtained for the global asymptotic stability of the endemic equilibrium. By comparison arguments, it is proved that if the basic reproduction number is less than unity, the disease-free equilibrium is globally asymptotically stable. Numerical simulations are carried out to illustrate the main theoretical results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beretta, E., Hara, T., Ma, W., Takeuchi, Y.: Global asymptotic stability of an SIR epidemic model with distributed time delay. Nonlinear Anal. 47, 4107–4115 (2001)
Beretta, E., Takeuchi, Y.: Global stability of an SIR epidemic model with time delays. J. Math. Biol. 33, 250–260 (1995)
Beretta, E., Takeuchi, Y.: Convergence results in SIR epidemic model with varying population sizes. Nonlinear Anal. 28, 1909–1921 (1997)
Capasso, V., Serio, G.: A generalization of the Kermack–McKendrick deterministic epidemic model. Math. Biosci. 42, 41–61 (1978)
Cooke, K., van den Driessche, P.: Analysis of an SEIRS epidemic model with two delays. J. Math. Biol. 35, 240–260 (1996)
Gakkhar, S., Negi, K.: Pulse vaccination in SIRS epidemic model with non-monotonic incidence rate. Chaos Solitons Fractals 35, 626–638 (2008)
Gao, S., Chen, L., Teng, Z.: Pulse vaccination of an SEIR epidemic model with time delay. Nonlinear Anal.: Real World Appl. 9, 599–607 (2008)
Gao, S., Teng, Z., Xie, D.: The effects of pulse vaccination on SEIR model with two time delays. Appl. Math. Comput. 201, 282–292 (2008)
Hale, J.: Theory of Functional Differential Equations. Springer, Heidelberg (1977)
Hethcote, H.W., van den Driessche, P.: An SIS epidemic model with variable population size and a delay. J. Math. Biol. 34, 177–194 (1995)
Hethcote, H.W., van den Driessche, P.: Two SIS epidemiologic models with delays. J. Math. Biol. 40, 3–26 (2000)
Jin, Y., Wang, W., Xiao, S.: An SIRS model with a nonlinear incidence rate. Chaos Solitons Fractals 34, 1482–1497 (2007)
Kuang, Y.: Delay Differential Equations with Applications in Population Dynamics. Academic Press, New York (1993)
Li, G., Jin, Z.: Global stability of an SEIR epidemic model with infectious force in latent, infected and immune period. Chaos Solitons Fractals 25, 1177–1184 (2005)
Liu, J., Zhou, Y.: Global stability of an SIRS epidemic model with transport-related infection. Chaos Solitons Fractals 40, 145–158 (2009)
Liu, W.M., Hethcote, H.W., Levin, S.A.: Dynamical behavior of epidemiological models with nonlinear incidence rates. J. Math. Biol. 25, 359–380 (1987)
Liu, W.M., Levin, S.A., Iwasa, Y.: Influence of nonlinear incidence rates upon the behavior of SIRS epidemiological models. J. Math. Biol. 23, 187–204 (1986)
Ma, W., Song, M., Takeuchi, Y.: Global stability of an SIR epidemic model with time delay. Appl. Math. Lett. 17, 1141–1145 (2004)
Ma, W., Takeuchi, Y., Hara, T., Beretta, E.: Permanence of an SIR epidemic model with distributed time delays. Tohoku Math. J. 54, 581–591 (2002)
Meng, X., Chen, L., Cheng, H.: Two profitless delays for the SEIRS epidemic disease model with nonlinear incidence and pulse vaccination. Appl. Math. Comput. 186, 516–529 (2007)
Pang, G., Chen, L.: A delayed SIRS epidemic model with pulse vaccination. Chaos Solitons Fractals 34, 1629–1635 (2007)
Shulgin, B., Stone, L., Agur, Z.: Pulse vaccination strategy in the SIR epidemic model. Bull. Math. Biol. 60, 1123–1148 (1998)
Takeuchi, Y., Ma, W.: Stability analysis on a delayed SIR epidemic model with density dependent birth process. Dyn. Contin. Discrete Impuls. Syst. 5, 171–184 (1999)
Takeuchi, Y., Ma, W., Beretta, E.: Global asymptotic properties of a SIR epidemic model with finite incubation time. Nonlinear Anal. 42, 931–947 (2000)
Wang, W.: Global behavior of an SEIRS epidemic model with time delays. Appl. Math. Lett. 15, 423–428 (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 10671209, 10531030) and the Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, State Education Ministry.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, R., Ma, Z. Global stability of a delayed SEIRS epidemic model with saturation incidence rate. Nonlinear Dyn 61, 229–239 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-009-9644-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-009-9644-3