Abstract
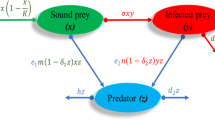
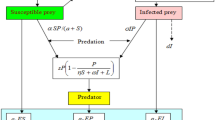
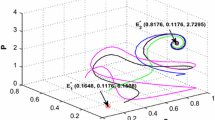
In the paper an eco-epidemic system with delay and parasitic infection in the prey is investigated. The conditions for asymptotic stability of steady states are derived and the length of the delay preserving the stability is also estimated. Further, the criterion for existence of Hopf-type small amplitude periodic oscillations of the predator and prey biomass is derived. Numerical results indicate that the delay does not affect the stability of the system in the process but makes all populations oscillate more intensively. In addition, the results show that the recovery makes the levels of the infected prey and the predator become lower but makes the sound prey higher in limit time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hudson, P.J., Dobson, A.P., Lafferty, K.D.: Is a healthy ecosystem one that is rich in parasites? Trends Ecol. Evol. 21, 381–385 (2006)
Grenfell, B.T., Dobson, A.P.: Ecology of Infectious Diseases in Natural Populations. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1995)
Hudson, P.J., Rizzoli, A., Grenfell, B.T., Heesterbeek, H., Dobson, A.P.: The Ecology of Wildlife Diseases. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2001)
Holt, R.D., Dobson, A.P., Begon, M., Bowers, R.G., Schauber, E.M.: Parasite establishment in host communities. Ecol. Lett. 6, 837–842 (2003)
Sait, S.M., Liu, W.C., Thompson, D.J., Godfrey, H.C.J., Begon, M.: Invasion sequence affects predator–prey dynamics in a multi-species interaction. Nature 405, 448–450 (2000)
Mukherjee, D.: A delayed prey–predator system with parasitic infection. Biosystems 85, 158–164 (2006)
Frank, M.H., Kirsten, S.: Disease-induced stabilization of predator–prey oscillations. J. Theor. Biol. 255, 299–306 (2008)
Martcheva, M.: Evolutionary consequences of predation for pathogens in prey. Bull. Math. Biol. 71, 819–844 (2009)
Xiao, N., Chen, L.: Modelling and analysis of a predator–prey model with disease in the prey. Math. Biosci. 171, 59–82 (2001)
Hadeler, K.P., Freedman, H.I.: Predator–prey populations with parasitic infection. J. Math. Biol. 27, 609–631 (1989)
Holt, R.D., Roy, M.: Predation can increase the prevalence of infectious disease. Am. Nat. 169, 690–699 (2007)
Han, L., Ma, Z., Hethcote, H.W.: Four predator prey models with infectious diseases. Math. Comput. Model. 34, 849–858 (2001)
Temple, S.A.: Do predators always capture substandard individuals disproportionately from prey populations? Ecology 68, 669–674 (1987)
Holmes, J.C., Bethel, W.M.: Modification of intermediate host behavior by parasites. In: E.V. Canning, C.A. Wright (Eds.) Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 51(Suppl. I), 123–149 (1972)
Hudson, P.J., Dobson, A.P., Newborn, D.: Do parasites make prey more vulnerable to predation? Red grouse and parasites. J. Anim. Ecol. 61, 681–692 (1992)
Packer, C., Holt, R.D., Hudson, P.J., Lafferty, K.D., Dobson, A.P.: Keeping the herds healthy and alert: implications of predator control for infectious disease. Ecol. Lett. 6, 797–802 (2003)
Hethcote, H.W., Wang, W., Han, L., Ma, Z.: A predator–prey model with infected prey. Theor. Popul. Biol. 66, 259–268 (2004)
Driessche, P., Watmough, J.: A simple SIS epidemic model with a backward bifurcation. J. Math. Biol. 40, 525–540 (2000)
Venturino, E.: Epidemics in predator–prey models: disease in the prey. In: Arino, O., Axelrod, D., Kimmel, M., Langlais, M. (Eds.) Mathematical Population Dynamics: Analysis of Heterogeneity. Theory of Epidemics, vol. 1, pp. 381–393. Wuerz Publishing, Winnipeg (1995)
Ji, X., Pei, Y., Li, C.: Two patterns of recruitment in an epidemic model with difference in immunity of individuals. Nonlinear Anal., Real World Appl. 11, 2078–2090 (2010)
Li, X., Wang, J., Ghosh, M.: Stability and bifurcation of an SIVS epidemic model with treatment and age of vaccination. Appl. Math. Model. 34(2), 437–450 (2010)
Li, Y., Cui, J.: The effect of constant and pulse vaccination on SIS epidemic models incorporating media coverage. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 14, 2353–2365 (2009)
Chen, J., Liu, X.: Stability of an seis epidemic model with constant recruitment and a varying total population size. Appl. Math. J. Chin. Univ. Ser. B 21(1), 1–8 (2006)
Li, C., Pei, Y., Liu, Z.: A prey–predator system with parasitic infection and recovery. J. Biomath. 25(1), 1–5 (2010)
Hatcher, M.J., Dick, J.T.A., Dunn, A.M.: How parasites affect interactions between competitors and predators. Ecol. Lett. 9, 1253–1271 (2006)
Castro, F.D., Bolker, B.M.: Parasite establishment and host extinction in model communities. OIKOS 111, 501–513 (2005)
Peterson, R.O., Page, R.E.: Wolf density as a predictor of predation rate. Swed. Wildlife Res. (Suppl.) 1, 771–773 (1987)
Freedman, H.I., Erbe, L.H., Rao, V.S.H.: Three species food chain model with mutual interference and time delays. Math. Biosci. 80, 57–80 (1986)
Hassard, B.D., Kazarinoff, N.D., Wan, Y.H.: Theory and Applications of Hopf-Bifurcation. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1981)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yongzhen, P., Shuping, L. & Changguo, L. Effect of delay on a predator–prey model with parasitic infection. Nonlinear Dyn 63, 311–321 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-010-9805-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-010-9805-4