Abstract
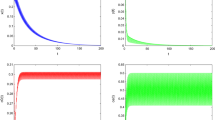
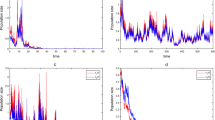
In this paper, we consider the genic mutation on an impulsive population system in polluted environment. All solutions of the investigated system are proved to be uniformly bounded. Using mathematical analysis methods, the conditions of the globally asymptotically stable population-extinction solution of the investigated system are obtained. The permanent condition of the investigated system is also obtained. Finally, numerical analysis is carried out illustrate our results. Our results provide reliable tactic basis for the practical biological resource management in polluted environment.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Epstein, S.S.: Control of chemical pollutants. Nature 228, 816–819 (1970)
Waxman, D., Peck, J.R.: Sex and adaptation in a changing environment. Genetics 153, 1041–1053 (1999)
Bello, Y., Waxman, D.: Near-periodic substitution and the genetic variance induced by environmental change. J. Theor. Biol. 239, 152–160 (2006)
Xin, W., et al.: Environmental factors and birth defect. Med. Philos. 28, 18–21 (2007) (in Chinese)
Hass, C.N.: Application of predator-prey models to disinfection. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 53, 378–386 (1981)
Hsu, S.B., Waltman, P.: Competition in the chemostat when one competitor produces a toxin. Jpn. J. Ind. Appl. Math. 15, 471–490 (1998)
Jenson, A.L., Marshall, J.S.: Application of surplus production model to access environmental impacts in exploited populations of Daphnia pluex in the laboratory. Environ. Pollut. A 28, 273–280 (1982)
De Luna, J.T., Hallam, T.G.: Effects of toxicants on population: a qualitative approach. IV. Resource-consumer-toxicants model. Ecol. Model. 35, 249–273 (1987)
Dubey, B.: Modelling the effect of toxicant on forestry resources. Indian J. Pure Appl. Math. 28, 1–12 (1997)
Freedman, H.I., Shukla, J.B.: Models for the effect of toxicant in a single-species and predator-prey systems. J. Math. Biol. 30, 15–30 (1991)
Hallam, T.G., Clark, C.E., Jordan, G.S.: Effects of toxicant on population: a qualitative approach II. First order kinetics. J. Math. Biol. 18, 25–37 (1983)
Zhang, B.G.: Population’s Ecological Mathematics Modeling. Publishing of Qingdao Marine University, Qingdao (1990)
Hallam, T.G., Clark, C.E., Lassider, R.R.: Effects of toxicant on population: a qualitative approach I. Equilibrium environmental exposure. Ecol. Model. 18, 291–340 (1983)
Liu, B., Chen, L.S., Zhang, Y.J.: The effects of impulsive toxicant input on a population in a polluted environment. J. Biol. Syst. 11, 265–287 (2003)
Caughley, G.: Analysis of Vertebrate Population. Wiley, New York (1977)
Tang, S., Chen, L.: Density-dependent birth rate, birth pulses and their population dynamics consequences. J. Math. Biol. 290, 185–199 (2002)
Liu, Z., Chen, L.: Periodic solution of a two-species competitive system with toxicant and birth pules. Chaos Solitons Fractals 32, 1703–1712 (2007)
Liu, X.N.: Impulsive stabilization and applications to population growth models. J. Math. 25(1), 381–395 (1995)
Lakshmikantham, V.: Theory of Impulsive Differential Equations. World Scientific, Singapore (1989)
Liu, X.N., Chen, L.S.: Complex dynamics of Holling II Lotka-Volterra predator-prey system with impulsive perturbations on the predator. Chaos Solitons Fractals 16, 311–320 (2003)
Song, X.Y., Chen, L.S.: Uniform persistence and global attractivity for nonautonomous competitive systems with dispersion. J. Syst. Sci. Complex. 15, 307–314 (2002)
Meng, X.Z., Chen, L.S.: Permanence and global stability in an impulsive Lotka-Volterra N-species competitive system with both discrete delays and continuous delays. Int. J. Biomath. 1(2), 179–196 (2008)
Jiao, J.J., et al.: An appropriate pest management SI model with biological and chemical control concern. Appl. Math. Comput. 196, 285–293 (2008)
Murray, J.D.: Mathematical Biology, 2nd corrected edn. Springer, Heidelberg (1993)
Takeuchi, Y.: Global Dynamical Properties of Lotka-Volterra Systems. World Scientific, Singapore (1996)
Takeuchi, Y., Oshime, Y., Matsuda, H.: Persistence and periodic orbits of a three-competitor model with refuges. Math. Biosci. 108(1), 105–125 (1992)
Kuang, Y.: Delay Differential Equation with Application in Population Dynamics, pp. 67–70. Academic Press, New York (1987)
Leung, A.W.: Optimal harvesting-coefficient control of stead-state prey-predator diffusive Volterra-Lotka system. Appl. Math. Optim. 31, 219–241 (1995)
Alvarez, H.R., Shepp, L.A.: Optimal harvesting of stochastically fluctuating populations. J. Math. Biol. 37, 155–177 (1998)
Tang, S.Y., Chen, L.S.: The effect of seasonal harvesting on stage-structured population models. J. Math. Biol. 48, 357–374 (2003)
Zhao, Z., Chen, L.S.: The effect of pulsed harvesting policy on the inshore-offshore fishery model with impulsive diffusion. Nonlinear Dyn. 63, 521–535 (2011)
Jiao, J.J., Ye, K.L., Chen, L.S.: Dynamical analysis of a five-dimensioned chemostat model with impulsive diffusion and pulse input environmental toxicant. Chaos Solitons Fractals 44, 17–27 (2011)
Jury, E.L.: Inners and Stability of Dynamics System. Wiley, New York (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (10961008), the Science Technology Foundation of Guizhou Education Department (2008038), and the Science Technology Foundation of Guizhou (2010J2130).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiao, J., Cai, S. & Chen, L. Dynamics of the genic mutational rate on a population system with birth pulse and impulsive input toxins in polluted environment. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 40, 445–457 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-012-0577-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-012-0577-5