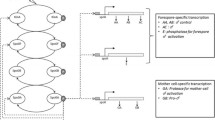
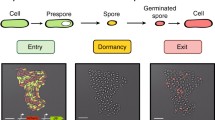
Abstract
Under conditions of nutrient deprivation, the Gram positive soil bacterium Bacillus subtilis can abandon vegetative growth and form a dormant, environmentally-resistant spore instead. The decision to either divide or sporulate is controlled by a large and complex genetic regulatory network integrating various environmental, cell-cycle, and metabolic signals. Although sporulation in B. subtilis is one of the best-understood model systems for prokaryotic development, very little quantitative data on kinetic parameters and molecular concentrations are available. A qualitative simulation method is used to model the sporulation network and simulate the response of the cell to nutrient deprivation. Using this method, we have been able to reproduce essential features of the choice between vegetative growth and sporulation, in particular the role played by competing positive and negative feedback loops.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antoniewski, C., B. Savelli and P. Stragier (1990). The spoIIJ gene, which regulates early developmental steps in Bacillus subtilis, belongs to a class of environmentally responsive genes. J. Bacteriol. 172, 86–93.
Bai, U. and I. Mandić-Mulec (1993). SinI modulates the activity of SinR, a developmental switch protein of Bacillus subtilis, by protein-protein interaction. Genes Dev. 7, 139–148.
Burbulys, D., K. A. Trach and J. A. Hoch (1991). Initiation of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis is controlled by a multicomponent phosphorelay. Cell 64, 545–552.
Burkholder, W. F. and A. D. Grossman (2000). Regulation of the initiation of endospore formation in Bacillus subtilis, in Prokaryotic Development, Y. V. Brun and L. J. Shimkets (Eds), Washington, DC: ASM, pp. 151–166.
Carter, H. L. 3rd and C. P. Moran Jr (1986). New RNA polymerase σ factor under spo0 control in Bacillus subtilis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 83, 9438–9442.
Chung, J. D., G. Stephanopoulos, K. Ireton and A. D. Grossman (1994). Gene expression in single cells of Bacillus subtilis: evidence that a threshold mechanism controls the initiation of sporulation. J. Bacteriol. 176, 1977–1984.
de Jong, H. (2002). Modeling and simulation of genetic regulatory systems: a literature review. J. Comput. Biol. 9, 69–105.
de Jong, H., J. Geiselmann, G. Batt, C. Hernandez, and M. Page (2002). Qualitative simulation of the initiation of sporulation in B. subtilis. Technical Report RR-4527, INRIA.
de Jong, H., J. Geiselmann, C. Hernandez and M. Page (2003a). Genetic network analyzer: qualitative simulation of genetic regulatory networks. Bioinformatics 19, 336–344.
de Jong, H., J.-L. Gouzé, C. Hernandez, M. Page, T. Sari and H. Geiselmann (2003b). Qualitative simulation of genetic regulatory networks using piecewise-linear models. Bull. Math. Biol. (this volume).
Dixon, L. G., S. Seredick, M. Richer and G. B. Spiegelman (2001). Developmental gene expression in Bacillus subtilis crsA47 mutants reveals glucose-activated control of the gene for the minor sigma factor σ H. J. Bacteriol. 183, 4814–4822.
Dubnau, D. and K. Turgay (2000). Regulation of competence in Bacillus subtilis and its relation to stress response, in Bacterial Stress Responses, G. Storz and R. Hengge-Aronis (Eds), Washington, DC: ASM, pp. 249–260.
Dubnau, E., J. Weir, G. Nair, L. Carter 3rd, C. P. Moran Jr and I. Smith (1988). Bacillus sporulation gene spo0H codes for σ 30(σ H). J. Bacteriol. 170, 1054–1062.
Errington, J. (2001). Septation and chromosome segregation during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 4, 660–666.
Eymann, C., G. Mittenhuber and M. Hecker (2001). The stringent response, σ H-dependent gene expression and sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Gen. Genet. 264, 913–923.
Fawcett, P., P. Eichenberger, R. Losick and P. Youngman (2000). The trancriptional profile of early to middle sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 8063–8068.
Ferrari, F. A., K. Trach, D. LeCoq, J. Spence, E. Ferrari and J. A. Hoch (1985). Characterization of the spo0A locus and its deduced product. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 82, 2647–2651.
Filippov, A. F. (1988). Differential Equations with Discontinuous Righthand Sides, Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Fort, P. and P. J. Piggot (1984). Nucleotide sequence of sporulation locus spoIIA in Bacillus subtilis. J. Gen. Microbiol. 130, 2147–2153.
Fujita, M. and Y. Sadaie (1998). Feedback loops involving Spo0A and AbrB in in vitro transcription of the genes involved in the initiation of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 124, 98–104.
Gaur, N. K., K. Cabane and I. Smith (1988). Structure and expression of the Bacillus subtilis sin operon. J. Bacteriol. 170, 1046–1053.
Gaur, N. K., E. Dubnau and I. Smith (1986). Characterization of a cloned Bacillus subtilis gene that inhibits sporulation in multiple copies. J. Bacteriol. 168, 860–869.
Gaur, N. K., J. Oppenheim and I. Smith (1991). The Bacillus subtilis sin gene, a regulator of alternate developmental processes, codes for a DNA-binding protein. J. Bacteriol. 173, 678–686.
Glass, L. and S. A. Kauffman (1973). The logical analysis of continuous non-linear biochemical control networks. J. Theor. Biol. 39, 103–129.
Gouzé, J.-L. and T. Sari (2003). A class of piecewise linear differential equations arising in biological models. Dynam. Syst. 17, 299–316.
Grimshaw, C. E., S. Huang, C. G. Hanstein, M. A. Strauch, D. Burbulys, L. Wang, J. A. Hoch and J. M. Whiteley (1998). Synergistic kinetic interactions between components of the phosphorelay controlling sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Biochemistry 37, 1365–1375.
Grossman, A. D. (1995). Genetic networks controlling the initiation of sporulation and the development of genetic competence in Bacillus subtilis. Ann. Rev. Genet. 29, 477–508.
Guespin-Michel, J. F. (1971). Phenotypic reversion in some early blocked sporulation mutants of Bacillus subtilis: isolation and phenotype identification of partial revertants. J. Bacteriol. 108, 241–247.
Haldenwang, W. G. (1995). The sigma factors of Bacillus subtilis. Microbiol. Rev. 59, 1–30.
Healy, J., J. Weir, I. Smith and R. Losick (1991). Post-transcriptional control of a sporulation regulatory gene encoding transcription factor σ H in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 5, 477–487.
Hecker, M. and U. Völker (2001). General stress response of Bacillus subtilis and other bacteria. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 44, 35–91.
Heinrich, R. and S. Schuster (1996). The Regulation of Cellular Systems, New York: Chapman & Hall.
Hoch, J. A. (1976). Genetics of bacterial sporulation. Adv. Genet. 18, 69–98.
Hoch, J. A. (1993). Regulation of the phosphorelay and the initiation of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 47, 441–465.
Jaacks, K. J., J. Healy, R. Losick and A. D. Grossman (1989). Identification and characterization of genes controlled by the sporulation-regulatory gene spo0H in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 171, 4121–4129.
Jiang, M., W. Shao, M. Perego and J. A. Hoch (2000). Multiple histidine kinases regulate entry into stationary phase and sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 38, 535–542.
Kallio, P. T., J. E. Fagelson, J. A. Hoch and M. A. Strauch (1991). The transition state regulator Hpr of Bacillus subtilis is a DNA-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 13411–13417.
Kauffman, S. A. (1993). The Origins of Order: Self-Organization and Selection in Evolution, New York: Oxford University Press.
Kohn, K. W. (2001). Molecular interaction maps as information organizers and simulation guides. Chaos 11, 1–14.
Kroos, L., B. Zhang, H. Ichikawa and Y.-T. N. Yu (1999). Control of σ factor activity during Bacillus subtilis sporulation. Mol. Microbiol. 31, 1285–1294.
Kudoh, J., T. Ikeuchi and K. Kurahashi (1985). Nucleotide sequences of the sporulation gene spo0A and its mutant genes of Bacillus subtilis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82, 2665–2668.
Lazazzera, B. A., I. G. Kurtser, R. S. McQuade and A. D. Grossman (1999). An autoregulatory circuit affecting peptide signaling in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 181, 5193–5200.
LeDeaux, J. R., N. Yu and A. D. Grossman (1995). Different roles for KinA, KinB, and KinC in the initiation of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 177, 861–863.
Levin, P. A. and A. D. Grossman (1998). Cell cycle and sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 1, 630–635.
Lewis, R. J., D. J. Scott, J. A. Brannigan, J. C. Ladds, M. A. Cervin, G. B. Spiegelman, J. G. Hoggett, I. Barak and A. J. Wilkinson (2002). Dimer formation and transcription activation in the sporulation response regulator Spo0A. J. Mol. Biol. 316, 235–245.
Louie, P., A. Lee, K. Stansmore, R. Grant, C. Ginther and T. Leighton (1992). Roles of rpoD, spoIIF, spoIIJ, spoIIN, and sin in regulation of Bacillus subtilis stage II sporulation-specific transcription. J. Bacteriol. 174, 3570–3576.
Mandić-Mulic, I., L. Doukhan and I. Smith (1995). The Bacillus subtilis SinR protein is a repressor of the key sporulation gene spo0A. J. Bacteriol. 177, 4619–4627.
Mandić-Mulec, I., N. Gaur, U. Bai and I. Smith (1992). Sin, a stage-specific repressor of cellular differentiation. J. Bacteriol. 174, 3561–3569.
Mendoza, L., D. Thieffry and E. R. Alvarez-Buylla (1999). Genetic control of flower morphogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana: a logical analysis. Bioinformatics 15, 593–606.
Mestl, T., E. Plahte and S. W. Omholt (1995). A mathematical framework for describing and analysing gene regulatory networks. J. Theor. Biol. 176, 291–300.
Moszer, I., L. M. Jones, S. Moreira, C. Fabry and A. Danchin (2002). SubtiList: the reference database for the Bacillus subtilis genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 30, 62–65.
Mueller, J. P., G. Bukusoglu and A. L. Sonenshein (1992). Transcriptional regulation of Bacillus subtilis glucose starvation-inducible genes: control of gsiA by the ComP-ComA signal transduction system. J. Bacteriol. 174, 4361–4373.
Perego, M. (1998). Kinase-phosphatase competition regulates Bacillus subtilis development. Trends Microbiol. 6, 366–370.
Perego, M., S. P. Cole, D. Burbulys, K. Trach and J. A. Hoch (1989). Characterization of the gene for a protein kinase which phosphorylates the sporulation-regulatory proteins Spo0A and Spo0F of Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 171, 6187–6196.
Perego, M. and J. A. Hoch (1987). Isolation and sequence of the spo0E gene: its role in initiation of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 1, 125–132.
Perego, M. and J. A. Hoch (1988). Sequence analysis of the hpr locus, a regulatory gene for protease production and sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 170, 2560–2567.
Perego, M. and J. A. Hoch (1991). Negative regulation of Bacillus subtilis sporulation by the spo0E gene product. J. Bacteriol. 173, 2514–2520.
Perego, M., G. B. Spiegelman and J. A. Hoch (1988). Structure of the gene for the transition state regulator, abrB: regulator synthesis is controlled by the spo0A sporulation gene in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 2, 689–699.
Perego, M., J. J. Wu, G. B. Spiegelman and J. A. Hoch (1991). Mutational dissociation of the positive and negative regulatory properties of the Spo0A sporulation transcription factor of Bacillus subtilis. Gene 100, 207–212.
Phillips, Z. E. and M. A. Strauch (2002). Bacillus subtilis sporulation and stationary phase gene expression. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 59, 392–402.
Plahte, E., T. Mestl and S. W. Omholt (1998). A methodological basis for description and analysis of systems with complex switch-like interactions. J. Math. Biol. 36, 321–348.
Predich, M., G. Nair and I. Smith (1992). Bacillus subtilis early sporulation genes kinA, spo0F, and spo0A are transcribed by the RNA polymerase containing σ H. J. Bacteriol. 174, 2771–2778.
Ptashne, M. (1992). A Genetic Switch: Phage λ and Higher Organisms, 2nd edn, Cambridge, MA: Cell Press & Blackwell Science.
Sánchez, L. and D. Thieffry (2001). A logical analysis of the Drosophila gap genes. J. Theor. Biol. 211, 115–141.
Segel, L. A. (1984). Modeling Dynamic Phenomena in Molecular and Cellular Biology, Cambridge, MA: Cambridge University Press.
Shafikhani, S. H., I. Mandic-Mulec, M. A. Strauch, I. Smith and T. Leighton (2002). Postexponential regulation of sin operon expression in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 184, 564–571.
Siranosian, K. J. and A. D. Grossman (1994). Activation of spo0A transcription by σ H is necessary for sporulation but not for competence in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 176, 3812–3815.
Smith, I. (1993). Regulatory proteins that control late-growth development, in Bacillus subtilis and other Gram-Positive Bacteria: Biochemistry, Physiology, and Molecular Genetics, A. L. Sonenshein, J. A. Hoch and R. Losick (Eds), Washington, DC: ASM, pp. 785–800.
Smith, I., I. Mandić-Mulec and N. Gaur (1991). The role of negative control in sporulation. Res. Microbiol. 142, 831–839.
Snoussi, E. H. (1989). Qualitative dynamics of piecewise-linear differential equations: a discrete mapping approach. Dyn. Stab. Syst. 4, 189–207.
Sonenshein, A. L. (2000a). Bacterial sporulation: a response to environmental signals, in Bacterial Stress Responses, G. Storz and R. Hengge-Aronis (Eds), Washington, DC: ASM, pp. 199–215.
Sonenshein, A. L. (2000b). Control of sporulation initiation in Bacillus subtilis. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 3, 561–566.
Stragier, P. and R. Losick (1996). Molecular genetics of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Ann. Rev. Genet. 30, 297–341.
Strauch, M. A. (1993a). AbrB, a transition state regulator, in Bacillus subtilis and other Gram-Positive Bacteria: Biochemistry, Physiology, and Molecular Genetics, A. L. Sonenshein, J. A. Hoch and R. Losick (Eds), Washington, DC: ASM, pp. 757–764.
Strauch, M. A. (1993b). Regulation of Bacillus subtilis gene expression during the transition from exponential growth to stationary phase. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 46, 121–153.
Strauch, M. A. and J. A. Hoch (1993). Transition-state regulators: sentinels of Bacillus subtilis post-exponential gene expression. Mol. Microbiol. 7, 337–342.
Strauch, M. A., G. B. Spiegelman, M. Perego, W. C. Johnson, D. Burbulys and J. A. Hoch (1989a). The transition state transcription regulator abrB of Bacillus subtilis is a DNA binding protein. EMBO J. 8, 1615–1621.
Strauch, M. A., M. Perego, D. Burbulys and J. A. Hoch (1989b). The transition state transcription regulator AbrB of Bacillus subtilis is autoregulated during vegetative growth. Mol. Microbiol. 3, 1203–1209.
Strauch, M. A., K. A. Trach, J. Day and J. A. Hoch (1992). Spo0A activates and represses its own synthesis by binding at its dual promoters. Biochimie 74, 619–626.
Thieffry, D. and R. Thomas (1995). Dynamical behaviour of biological networks: II. Immunity control in bacteriophage lambda. Bull. Math. Biol. 57, 277–297.
Thomas, R. and R. d’Ari (1990). Biological Feedback, Boc Raton, FL: CRC Press.
Trach, K. et al. (1991). Control of the initiation of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis by a phosphorelay. Res. Microbiol. 142, 815–823.
Trach, K. A. and J. A. Hoch (1993). Multisensory activation of the phosphorelay initiating sporulation in Bacillus subtilis: identification and sequence of the protein kinase of the alternate pathway. Mol. Microbiol. 8, 69–79.
Vaughn, J. L., V. Feher, S. Naylor, M. A. Strauch and J. Cavanagh (2000). Novel DNA binding domain and genetic regulation model of Bacillus subtilis transition state regulator abrB. Nat. Struct. Biol. 7, 1139–1146.
Wang, L., R. Grau, M. Perego and J. A. Hoch (1997). A novel histidine kinase inhibitor regulating development in Bacillus subtilis. Genes Dev. 11, 2569–2579.
Weir, J., E. Dubnau, N. Ramakrishna and I. Smith (1984). Bacillus subtilis spo0H gene. J. Bacteriol. 157, 405–412.
Weir, J., M. Predich, E. Dubnau, G. Nair and I. Smith (1991). Regulation of spo0H, a gene coding for the Bacillus subtilis σ H factor. J. Bacteriol. 173, 521–529.
Wu, J.-J., M. G. Howard and P. J. Piggot (1989). Regulation of transcription of the Bacillus subtilis spoIIA locus. J. Bacteriol. 171, 692–698.
Wu, J.-J., P. J. Piggot, K. M. Tatti and C. P. Moran Jr (1991). Transcription of the Bacillus subtilis spoIIA locus. Gene 101, 113–116.
Yagil, G. and E. Yagil (1971). On the relation between effector concentration and the rate of induced enzyme synthesis. Biophys. J. 11, 11–27.
Yamashita, S., F. Kawamura, H. Yoshikawa, H. Takahashi, Y. Kobayashi and H. Saito (1989). Dissection of the expression signals of the spo0A gene of the Bacillus subtilis: glucose represses sporulation-specific expression. J. Gen. Microbiol. 135, 1335–1345.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Jong, H., Geiselmann, J., Batt, G. et al. Qualitative simulation of the initiation of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis . Bull. Math. Biol. 66, 261–299 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bulm.2003.08.009
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bulm.2003.08.009