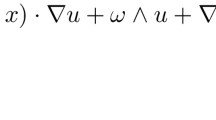Abstract
Let ℬ be a body immersed in a Navier-Stokes liquid ℒ that fills the whole space. Assume that ℬ rotates with prescribed constant angular velocity ω. We show that if the magnitude of ω is not “too large”, there exists one and only one corresponding steady motion of ℒ such that the velocity field v(x) and its gradient grad v(x) decay like |x|−1 and |x|−2, respectively. Moreover, the pressure field p(x) and its gradient grad p(x) decay like |x|−2 and |x|−3, respectively. These solutions are “physically reasonable” in the sense of Finn. In particular, they are unique and satisfy the energy equation. This result is relevant to several applications, including sedimentation of heavy particles in a viscous liquid.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Adams, Sobolev Spaces. Academic Press, New York (1975).
A.S. Advani, Flow and Rheology in Polymer Composites Manufacturing. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1994).
K.I. Babenko, On stationary solutions of the problem of flow past a body of a viscous incompressible fluid. Mat. Sb. 91(133) (1973) 3–27; English transl.: Math. SSSR-Sb. 20 (1973) 1–25.
W. Borchers, Zur Stabilität und Faktorisierungsmethode für die Navier-Stokes Gleichungen inkompressibler viskoser Flüssigkeiten. Habilitationsschrift, University of Paderborn (1992).
Z.-M. Chen and T. Miyakawa, Decay properties of weak solutions to a perturbed Navier-Stokes system in Rn. Adv.Math. Sci. Appl. 7(2) (1997) 741–770.
R.G. Cox, The steady motion of a particle of arbitrary shape at small Reynolds numbers. J. Fluid Mech. 23 (1965) 625–643.
P. Deuring, On H 2-estimates of solutions to the Stokes system with an artificial boundary condition. J. Math. Fluid Mech. 4 (2002) 203–236.
P. Deuring and G.P. Galdi, On the asymptotic behavior of physically reasonable solutions to the stationary Navier-Stokes system in three-dimensional exterior domains with zero velocity at infinity. J. Math. Fluid Mech. 2(4) (2000) 353–364.
R. Finn, On the exterior stationary problem for the Navier-Stokes equations, and associated perturbation problems. Arch. Rational Mech. Anal. 19 (1965) 363–406.
H. Fujita, On the existence and regularity of the steady-state solutions of the Navier-Stokes equation. J. Fac. Sci. Univ. Tokyo (1A) 2 (1961) 59–102.
G.P. Galdi, An Introduction to the Mathematical Theory of the Navier-Stokes Equations: Linearized Steady Problems, revised edn. Springer Tracts Nat. Philos. 38. Springer-Verlag, New York (1998).
G.P. Galdi, An Introduction to the Mathematical Theory of the Navier-Stokes Equations: Nonlinear Steady Problems, revised edn. Springer Tracts Nat. Philos. 39. Springer-Verlag, New York (1998).
G.P. Galdi, Slow motion of a body in a viscous incompressible fluid with application to particle sedimentation. In: V.A. Solonnikov (ed.), Developments in Partial Differential Equations. Quaderni di Matematica della II Università di Napoli 2 (1998) 2–50.
G.P. Galdi, On the motion of a rigid body in a viscous liquid: A mathematical analysis with applications. In: S. Friedlander and D. Serre (eds), Handbook of Mathematical Fluid Mechanics. Elsevier Science (2002) pp. 653–791.
G.P. Galdi, J.G. Heywood and Y. Shibata, On the global existence and convergence to steady state of Navier-Stokes flow past an obstacle that is started from rest. Arch. Rational Mech. Anal. 138 (1997) 307–318.
G.P. Galdi and A. Vaidya, Translational steady fall of symmetric bodies in a Navier-Stokes liquid, with application to particle sedimentation. J. Math. Fluid Mech. 3(1) (2001) 183–211.
R.B. Guenther, R.T. Hudspeth and E.A. Thomann, Hydrodynamic forces on submerged rigid bodies - steady flow. J. Math. Fluid Mech. (2002), in press.
T. Hishida, An existence theorem for the Navier-Stokes flow in the exterior of a rotating obstacle. Arch. Rational. Mech. Anal. 150 (1999) 307–348.
T. Hishida, The Stokes operator with rotation effect in exterior domains. Analysis (Munich) 19 (1999) 51–67.
D.D. Joseph, Flow induced microstructure in Newtonian and viscoelastic fluids. In: Proceedings of the Fifth World Congress of Chemical Engineering. Particle Technology Track. 6 (1996) 3–16.
G. Kirchhoff, Ñber die Bewegung eines Rotationskörpers in einer Flüssigkeit. J. Reine Ang. Math. 71 (1869) 237–281.
O.A. Ladyzhenskaya, Investigation of the Navier-Stokes equation for a stationary flow of an incompressible fluid. Uspekhi Mat. Nauk. 14(3) (1959) 75–97 (in Russian).
O.A. Ladyzhenskaya, N.N. Ural'ceva and V.A. Solonnikov, Linear and Quasilinear Equations of Parabolic Type. Transl. Math. Monographs 23. Amer. Math. Soc., Providence, RI (1968).
H. Lamb, Hydrodynamics, Cambridge Univ. Press (1932).
J. Leray, Etude de diverses équations intégrales non linéaires et de quelques problèmes que pose l'hydrodynamique. J. Math. Pures Appl. 12 (1933) 1–82.
J. Leray, Sur le mouvement d'un liquide visqueux emplissant l'espace. Acta Math. 63 (1934) 193–248.
S.A. Nazarov and K. Pileckas, On steady Stokes and Navier-Stokes problems with zero velocity at infinity in a three-dimensional exterior domain. J. Math. Kyoto Univ. 40(3) (2000) 475–492.
S.A. Nazarov and M. Specovius-Neugebauer, Approximation of exterior boundary value problems for the Stokes system. Asymptotic Anal. 14(3) (1997) 223–255.
A. Novotný and M. Padula, Note on decay of solutions of steady Navier-Stokes equations in 3-D exterior domains. Differential Integral Equations 8(7) (1995) 1833–1842.
F.K.G. Odqvist, Ñber die Randwertaufgaben der Hydrodynamik Zäher Flüssigkeiten. Math. Z. 32 (1930) 329–375.
C.W. Oseen, Neuere Methoden und Ergebnisse in der Hydrodynamik. Akad. Verlagsgesellschaft M.B.H., Leipzig (1927).
H. Schmid-Schonbein and R. Wells, Fluid drop-like transition of erythrocytes under shear. Science 165(3890) (1969) 288–291.
D. Serre, Chute libre d'un solid dans un fluide visqueux incompressible. Existence. Japan J. Appl. Math. 40(1) (1987) 99–110.
C.G. Simader and H. Sohr, The Dirichlet Problem for the Laplacian in Bounded and Unbounded Domains. Pitman Res. Notes Math. Ser. 360. Longman Sc. Tech. (1997).
G. Stokes, On the effect of internal friction of fluids on the motion of pendulums. Trans. Cambridge Phil. Soc. 9 (1851) 8–85.
B. Tinland, L. Meistermann and G.Weill, Simultaneous measurements of mobility, dispersion, and orientation of DNA during steady-field gel electrophoresis coupling a fluorescence recovery after photobleaching apparatus with a fluorescence detected linear dichroism setup. Phys. Rev. E 61(6) (2000) 6993–6998.
W. Thomson and P.G. Tait, Natural Philosophy, Vols. 1, 2. Cambridge Univ. Press (1879).
C. Truesdell and W. Noll, Handbuch der Physik, Vol. VIII/3. Springer-Verlag (1965).
H.F. Weinberger, On the steady fall of a body in a Navier-Stokes fluid. Proc. Sympos. Pure Math. 23 (1973) 421–440.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galdi, G.P. Steady Flow of a Navier-Stokes Fluid Around a Rotating Obstacle. Journal of Elasticity 71, 1–31 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:ELAS.0000005543.00407.5e
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:ELAS.0000005543.00407.5e